LZ-Opticks-NVIDIA OptiX 6->7 : Notes
Progress
- Foundry based CSG geometry model
- only ~4 GPU allocations for all Solids
- brought in the many more basis shapes
- including : ellipsoid, plane defined convexpolyhedron
- migrated CSG to this geometry model : intersect_tree.h intersect_node.h
- easily testable on CPU (tests/ScanTest.sh)
- Clustered Sphere Issue : split geometry in one GAS ?
NEXT STEPS:
- split off CSG package used by OptiXTest(OptiX 7)
- get OptiX 6 to work with new CSG geometry model -> less code to maintain (during transition)
- Interface with Opticks : GMergedMesh -> Node,Prim,Plan,Tran -> SBT records
- performance tests with full geometries, try different approaches:
- For "global" non-repeated : one big remainder GAS ? Or split up into many GAS ?
- Reference all GAS (repeats and singles) from one IAS, or multi-IAS ?
- performance tests with full geometries, try different approaches:
"Foundry" based CSG geometry model : Solid/Prim/Node
Foundry : Solids + constituents
23 struct Foundry
24 {
...
97 void upload();
...
101 std::vector<Solid> solid ;
102 std::vector<Prim> prim ;
103 std::vector<Node> node ;
104 std::vector<float4> plan ;
105 std::vector<qat4> tran ;
106 std::vector<qat4> itra ;
107
108 Solid* d_solid ;
109 Prim* d_prim ;
110 Node* d_node ;
111 float4* d_plan ;
112 qat4* d_tran ;
113 qat4* d_itra ;
114 };
All solids+constituents created via Foundry (ref by index)
- Solid : 1 or more Prim : ( Solid -> GAS )
- Prim : 1 or more Node : (Prim ~ G4VSolid)
- (nodeOffset, numNode) -> SBT HitGroup record
- Node : CSG constituents
- basis shapes : sphere, box3, cone, cylinder, ...
- boolean operators : union, intersection, difference
- qat4 : scale-rotate-translate transform
- float4 : planes (normal + distance to origin)
Node Examples:
- Ellipsoid : sphere with scale transform
- ConvexPolyhedron_Tetrahedron : (planeIdx, numPlanes)
- Foundry::upload
all solids in geometry -> only four GPU allocations
- d_prim, d_node, d_plan, d_itra
https://github.com/simoncblyth/OptiXTest/blob/main/Foundry.h https://github.com/simoncblyth/OptiXTest/blob/main/qat4.h
OptiX 7 Intersect Prim (numNode, nodeOffset) ~ HitGroupData
CSG Node : 4 quads
union quad // cross-type convenience
{
float4 f ;
int4 i ;
uint4 u ;
};
struct Node
{
quad q0 ;
quad q1 ;
quad q2 ;
quad q3 ;
__device__
unsigned typecode() const { return q2.u.w ; }
};
struct HitGroupData // effectively Prim
{
int numNode ;
int nodeOffset ;
};
150 extern "C" __global__ void __intersection__is()
151 {
152 HitGroupData* hg = (HitGroupData*)optixGetSbtDataPointer();
153 int numNode = hg->numNode ;
154 int nodeOffset = hg->nodeOffset ;
155
156 const Node* node = params.node + nodeOffset ;
157 const float4* plan = params.plan ;
158 const qat4* itra = params.itra ;
159
160 const float t_min = optixGetRayTmin() ;
161 const float3 ray_origin = optixGetObjectRayOrigin();
162 const float3 ray_direction = optixGetObjectRayDirection();
163
164 float4 isect ;
165 if(intersect_prim(isect, numNode, node, plan, itra,
t_min , ray_origin, ray_direction ))
166 {
167 const unsigned hitKind = 0u ;
168 unsigned a0, a1, a2, a3;
169
170 a0 = float_as_uint( isect.x );
171 a1 = float_as_uint( isect.y );
172 a2 = float_as_uint( isect.z );
173 a3 = float_as_uint( isect.w ) ;
174
175 optixReportIntersection( isect.w, hitKind, a0, a1, a2, a3 );
176 }
177 }
- nodeOffset : points to first Node in tree of numNode
Prim : 1 or more Node : Holds AABB
Prim + PrimSpec
53 struct Prim
54 {
55 quad q0 ;
56 quad q1 ;
57 quad q2 ;
58 quad q3 ;
..
88 #if defined(__CUDACC__) || defined(__CUDABE__)
89 #else
91 static PrimSpec MakeSpec(
const Prim* prim0,
unsigned primIdx,
unsigned numPrim );
92 #endif
94 };
08 struct PrimSpec
9 {
10 const float* aabb ;
11 const unsigned* sbtIndexOffset ;
12 unsigned num_prim ;
13 unsigned stride_in_bytes ;
14 bool device ;
22 };
| q | x | y | z | w |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| q0 | numNode | nodeOffset | tranOffset | planOffset |
| q1 | sbtIndexOffset | |||
| q2 | BBMin_x | BBMin_y | BBMin_z | BBMax_x |
| q3 | BBMax_y | BBMax_z |
- Foundry::upload -> d_prim (array of Prim on device)
- Foundry::getPrimSpecDevice -> PrimSpec -> GAS
- avoids separate AABB allocations for all GAS
36 PrimSpec Prim::MakeSpec( const Prim* prim0,
unsigned primIdx,
unsigned numPrim ) // static
37 {
38 const Prim* prim = prim0 + primIdx ;
40 PrimSpec ps ;
41 ps.aabb = prim->AABB() ;
42 ps.sbtIndexOffset = prim->sbtIndexOffsetPtr() ;
43 ps.num_prim = numPrim ;
44 ps.stride_in_bytes = sizeof(Prim);
45 return ps ;
46 } // used on CPU to give device side pointers offset from d_prim
167 PrimSpec Foundry::getPrimSpecDevice(unsigned solidIdx) const
168 {
170 const Solid* so = solid.data() + solidIdx ;
171 return Prim::MakeSpec( d_prim, so->primOffset, so->numPrim ) ;;
174 }
Node : 4x4x32bit : 6 float params, 6 float AABB, 4 ints : typecode/gtranformIdx/boundary/index
sp:sphere zs:zsphere cy:cylinder ds:disc cn:cone hy:hyperboloid pl:plane sl:slab cx:convexpolyhedron b3:box3
| q | x | y | z | w | notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q0 | sp/zs/cy:cen_x cn:r1 hy:r0 z=0 waist b3:fx pl/sl:nx cx:planeIdx |
sp/zs/cy:cen_y cn:z1 hy:zf b3:fy pl/sl:ny cx:planeNum |
sp/zs/cy:cen_z cn:r2 hy:z1 b3:fz pl/sl:nz ds:inner_r | sp/zs/cy:radius cn:z2 hy:z2 pl:d ds:radius |
cn:z2 > z1 hy:z2 > z1 b3: fullside dimensions, center always origin |
| q1 | zs:zdelta_0 sl:a cy:z1 ds:z1 | zs:zdelta_1 sl:b cy:z2 ds:z2 | boundary | index | sl:a,b offsets from origin cy:z2 > z1 |
| q2 | BBMin_x | BBMin_y | BBMin_z | BBMax_x | q2.w was previously typecode |
| q3 | BBMax_y | BBMax_z | typecode | gtransformIdx complement |
intersect_prim -> intersect_node/intersect_tree
1089 INTERSECT_FUNC
1090 bool intersect_prim( float4& isect, int numNode, const Node* node, const float4* plan, const qat4* itra,
const float t_min , const float3& ray_origin, const float3& ray_direction )
1091 {
1092 return numNode == 1
1093 ?
1094 intersect_node(isect, node, plan, itra, t_min, ray_origin, ray_direction )
1095 :
1096 intersect_tree(isect, numNode, node, plan, itra, t_min, ray_origin, ray_direction )
1097 ;
1098 }
Intersection maths : intersect_node.h intersect_tree.h -> allows testing on CPU with tests/ScanTest.cc
https://github.com/simoncblyth/OptiXTest/blob/main/intersect_node.h
https://github.com/simoncblyth/OptiXTest/blob/main/intersect_tree.h
intersect_node : handling scale-rotate-translate transforms and complemented "inside-out" solids
1028 bool intersect_node( float4& isect, const Node* node, const float4* plan, const qat4* itra, const float t_min ,
const float3& ray_origin , const float3& ray_direction )
1029 {
1030 const unsigned typecode = node->typecode() ;
1031 const unsigned gtransformIdx = node->gtransformIdx() ;
1032 const bool complement = node->complement();
1034 const qat4* q = gtransformIdx > 0 ? itra + gtransformIdx - 1 : nullptr ; // gtransformIdx is 1-based, 0 meaning None
1036 float3 origin = q ? q->right_multiply(ray_origin, 1.f) : ray_origin ;
1037 float3 direction = q ? q->right_multiply(ray_direction, 0.f) : ray_direction ;
....
1055 bool valid = false ;
1056 switch(typecode)
1057 {
1058 case CSG_SPHERE: valid = intersect_node_sphere( isect, node->q0, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1059 case CSG_ZSPHERE: valid = intersect_node_zsphere( isect, node->q0, node->q1, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1060 case CSG_CONVEXP: valid = intersect_node_convexp( isect, node, plan, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1061 case CSG_CONE: valid = intersect_node_cone( isect, node->q0, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1062 case CSG_HYPERB: valid = intersect_node_hyperb( isect, node->q0, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1063 case CSG_BOX3: valid = intersect_node_box3( isect, node->q0, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1064 case CSG_PLANE: valid = intersect_node_plane( isect, node->q0, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1065 case CSG_SLAB: valid = intersect_node_slab( isect, node->q0, node->q1, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1066 case CSG_CYLINDER: valid = intersect_node_cylinder(isect, node->q0, node->q1, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1067 case CSG_DISC: valid = intersect_node_disc( isect, node->q0, node->q1, t_min, origin, direction ) ; break ;
1068 }
1069 if(valid && q ) q->left_multiply_inplace( isect, 0.f ) ;
// normals transform with inverse-transform-transposed -> left_multiply
1076 if(complement){ isect.x = -isect.x ; isect.y = -isect.y ; isect.z = -isect.z ; }
// flip complement normal, even for miss need to signal the complement with a -0.f
1082 return valid ;
1083 }
intersect_tree : Boolean CSG implementation : tranche slices of postorder sequence...
https://github.com/simoncblyth/OptiXTest/blob/main/intersect_tree.h
10 #include "error.h"
11 #include "tranche.h"
12 #include "csg.h"
13 #include "postorder.h"
14 #include "pack.h"
15 #include "csg_classify.h"
16
19 bool intersect_tree( float4& isect,
int numNode,
const Node* node,
const float4* plan0,
const qat4* itra0,
const float t_min ,
const float3& ray_origin,
const float3& ray_direction
)
20 {
21 unsigned height = TREE_HEIGHT(numNode) ; // 1->0, 3->1, 7->2, 15->3, 31->4
22 float propagate_epsilon = 0.0001f ; // ?
23 int ierr = 0 ;
24
25 LUT lut ;
26 Tranche tr ;
27 tr.curr = -1 ;
29 unsigned fullTree = PACK4(0,0, 1 << height, 0 ) ; // leftmost: 1<<height, root:1>>1 = 0 ("parent" of root)
30
35 tranche_push( tr, fullTree, t_min );
37 CSG_Stack csg ;
38 csg.curr = -1 ;
39 int tloop = -1 ;
40
41 while (tr.curr > -1)
42 {
..
CSG Parade Grid 1
CSG Parade Grid 2
CSG Working
CSG Boolean Parade Grid
Clustered Sphere Issue : Testing split shapes in single GAS

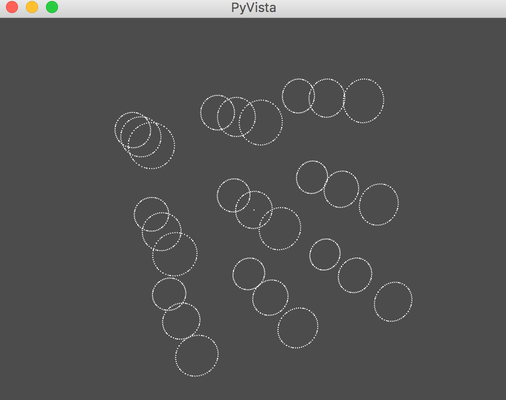
Expecting 9 spheres (CPU ScanTest "PyVista" view on right)
- see only one sphere ? Using 1 GAS with 1 BI with 9 AABB
- is there some "containment" requirement for the AABB in a GAS ?
"Extra" Background Slides Follow
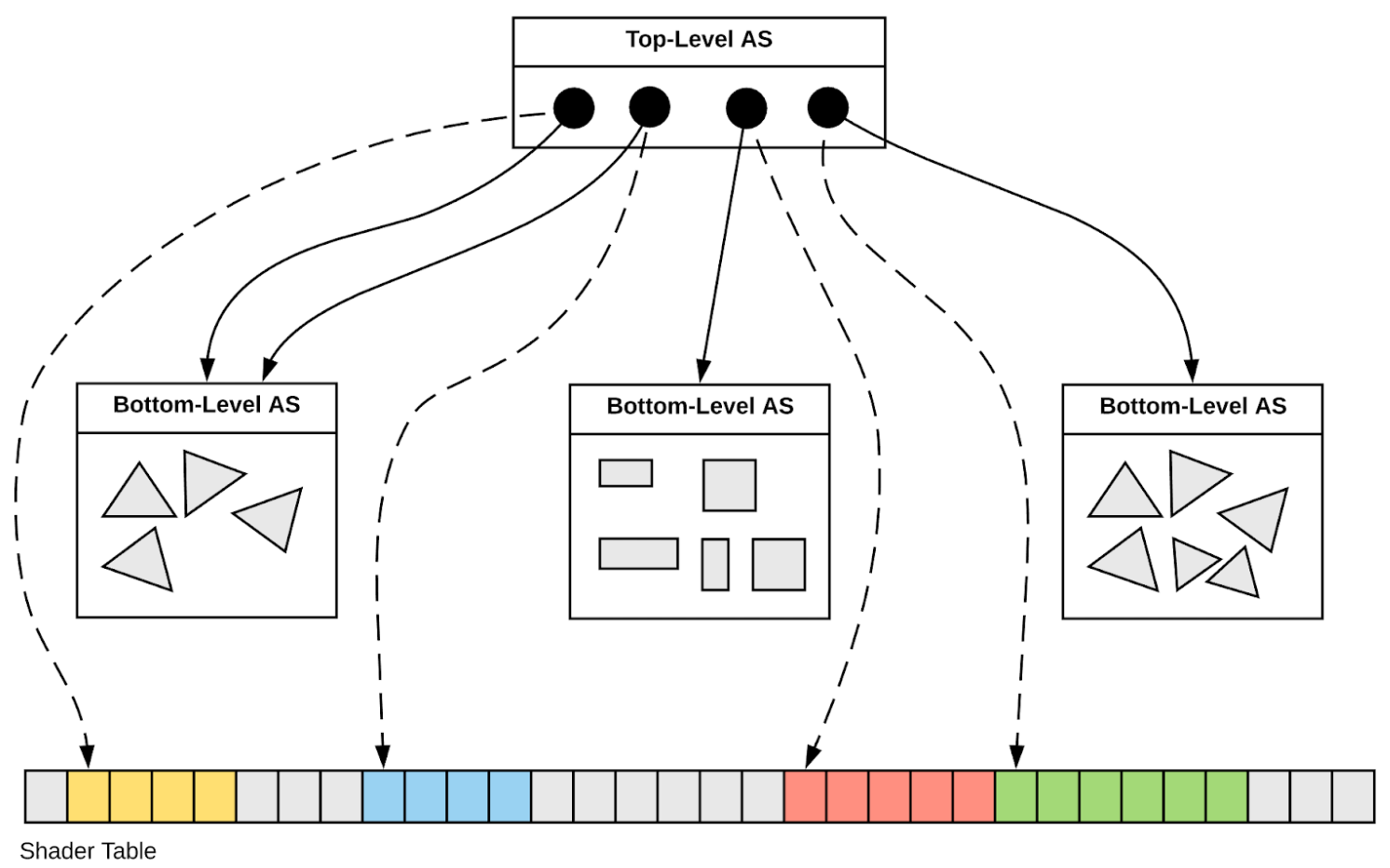
Two-Level Hierarchy : Instance transforms (TLAS) over Geometry (BLAS)
OptiX supports multiple instance levels : IAS->IAS->GAS BUT: Simple two-level is faster : works in hardware RT Cores
- AS
- Acceleration Structure
- TLAS (IAS)
- 4x4 transforms, refs to BLAS
- BLAS (GAS)
- triangles : vertices, indicescustom primitives : AABB
- AABB
- axis-aligned bounding box
SBT : Shader Binding Table
Flexibly binds together:
- geometry objects
- shader programs
- data for shader programs
Hidden in OptiX 1-6 APIs
Optimizing Geometry : Split BLAS to avoid overlapping bbox
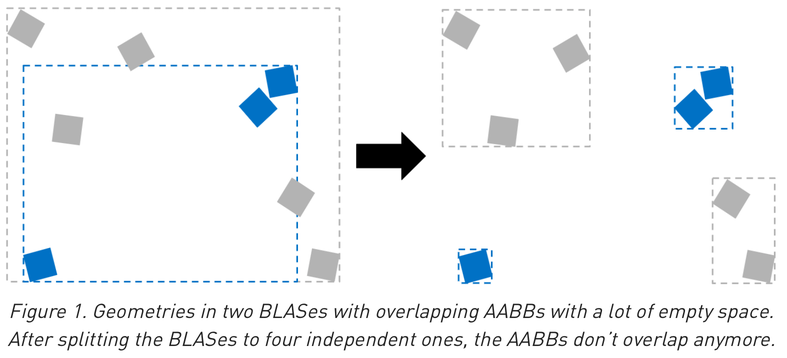
Optimization : deciding where to draw lines between:
- structure and solid (IAS and GAS)
- solids within GAS (bbox choice to minimize traversal intersection tests)
Where those lines are drawn defines the AS
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/best-practices-using-nvidia-rtx-ray-tracing/
Optimizing Geometry : Merge BLAS when lots of overlaps
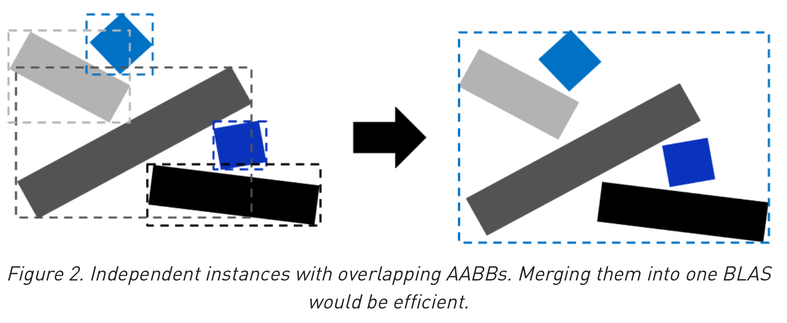
- lots of overlapping forces lots of intersections to find closest
- but too few bbox means the AS cannot help to avoid intersect tests
- balance required : needs experimentation and measurement to optimize
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/best-practices-using-nvidia-rtx-ray-tracing/
Ray Intersection with Transformed Object -> Geometry Instancing
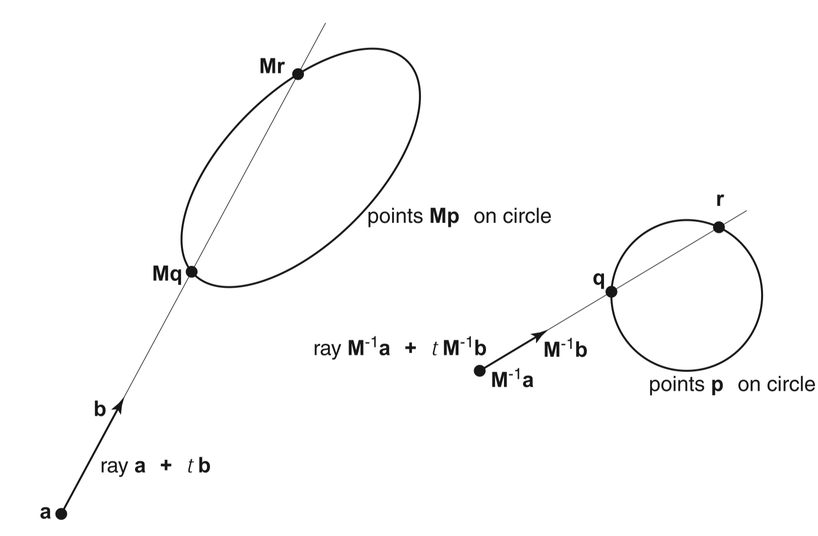
Fig 13.5 "Realistic Ray Tracing", Peter Shirley
Advantages apply equally to acceleration structures
Equivalent Intersects -> same t
- ray with ellipsoid : M*p
- M-1 ray with sphere : p
Local Frame Advantages
- simpler intersect (sphere vs ellipsoid)
- closer to origin -> better precision
Geometry Instancing Advantages
- many objects share local geometry
- orient+position with 4x4 M
- huge VRAM saving, less to copy
Requirements
- must not normalize ray direction
- normals transform differently
- N' = N * M-1T
- (due to non-uniform scaling)
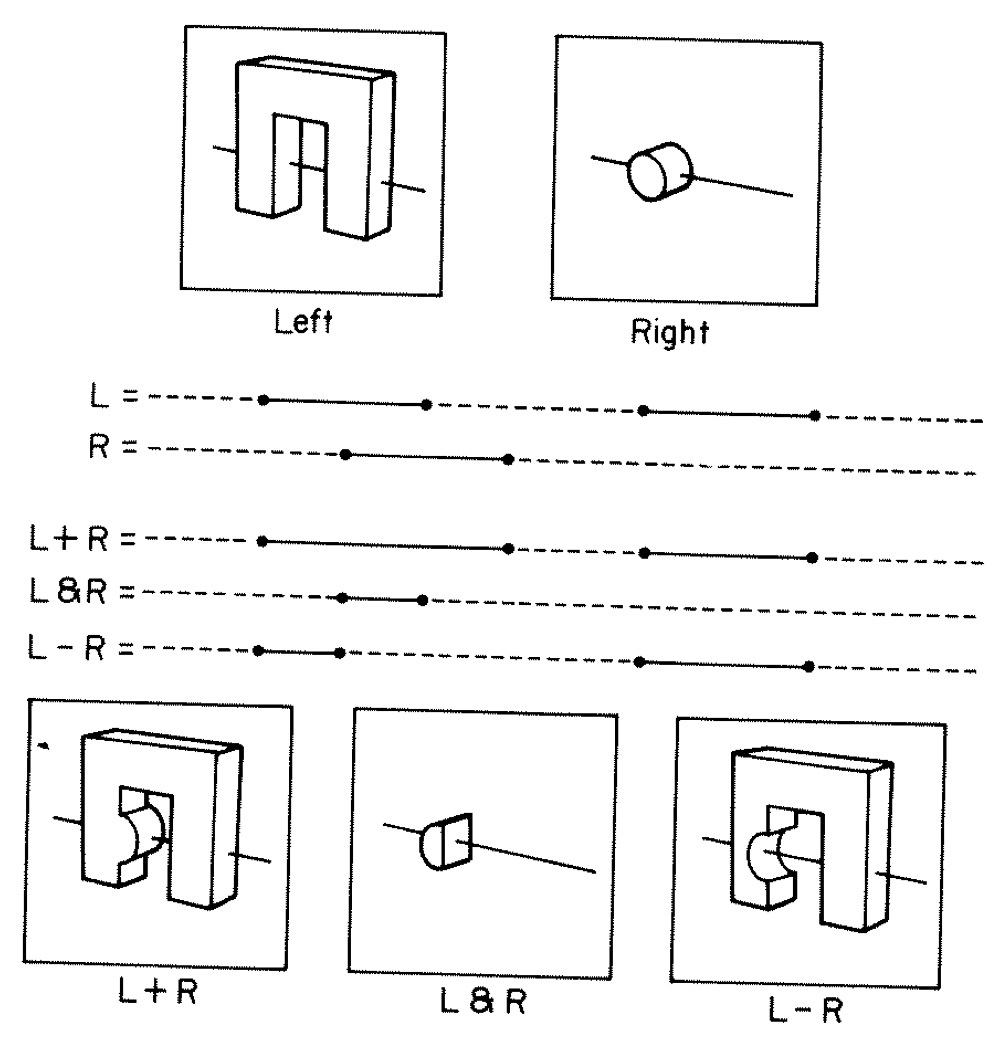
G4Boolean -> CUDA/OptiX Intersection Program Implementing CSG
Outside/Inside Unions
dot(normal,rayDir) -> Enter/Exit
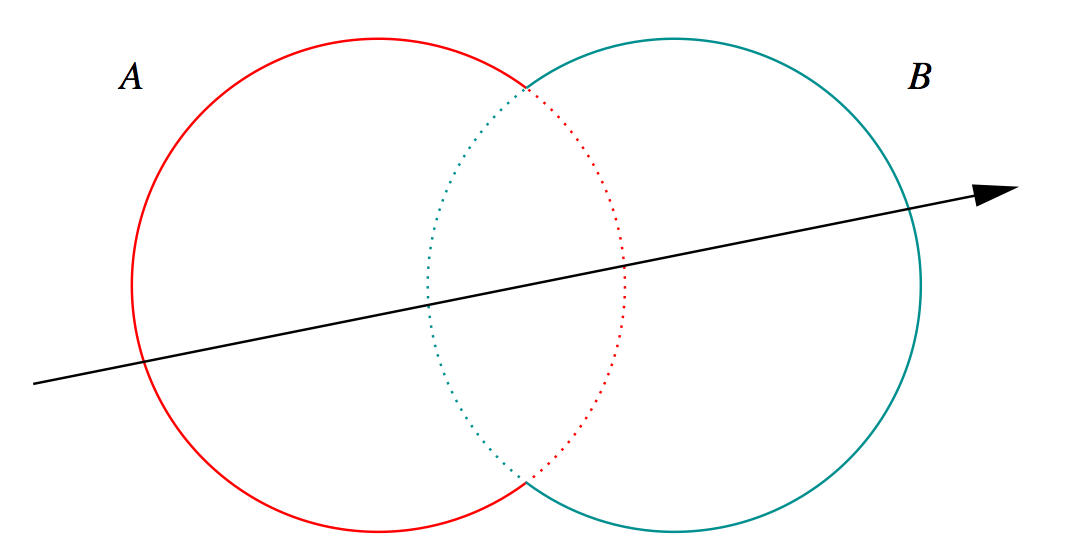
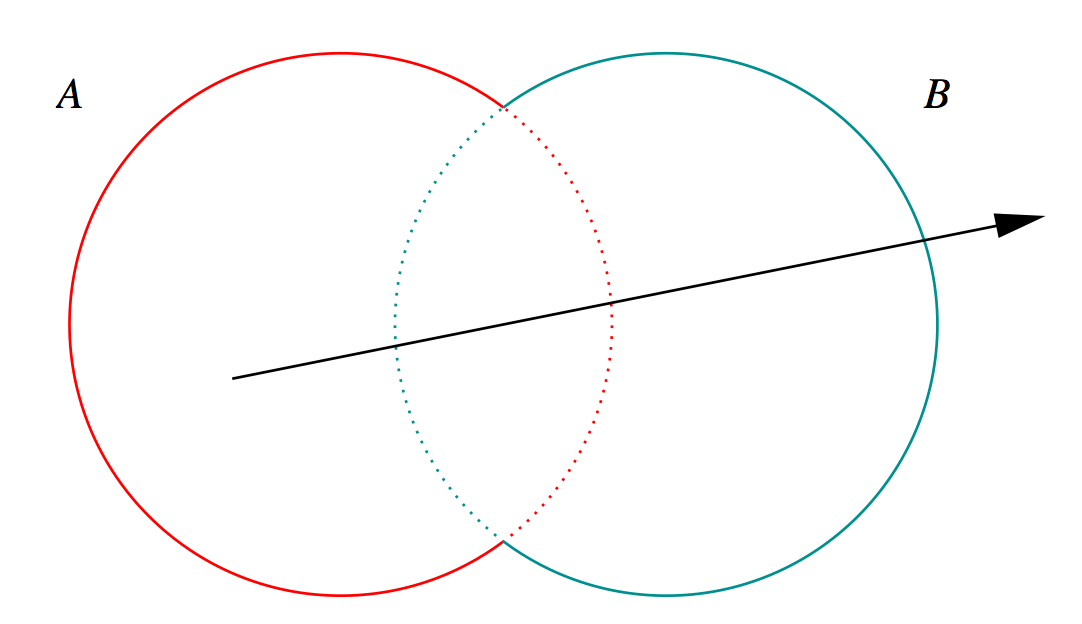
- A + B boundary not inside other
- A * B boundary inside other
Complete Binary Tree, pick between pairs of nearest intersects:
| UNION tA < tB | Enter B | Exit B | Miss B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enter A | ReturnA | LoopA | ReturnA |
| Exit A | ReturnA | ReturnB | ReturnA |
| Miss A | ReturnB | ReturnB | ReturnMiss |
- Nearest hit intersect algorithm [1] avoids state
- sometimes Loop : advance t_min , re-intersect both
- classification shows if inside/outside
- Evaluative [2] implementation emulates recursion:
- recursion not allowed in OptiX intersect programs
- bit twiddle traversal of complete binary tree
- stacks of postorder slices and intersects
- Identical geometry to Geant4
- solving the same polynomials
- near perfect intersection match
- [1] Ray Tracing CSG Objects Using Single Hit Intersections, Andrew Kensler (2006)
- with corrections by author of XRT Raytracer http://xrt.wikidot.com/doc:csg
- [2] https://bitbucket.org/simoncblyth/opticks/src/tip/optixrap/cu/csg_intersect_boolean.h
- Similar to binary expression tree evaluation using postorder traverse.
Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) : Shapes defined "by construction"
CSG Binary Tree
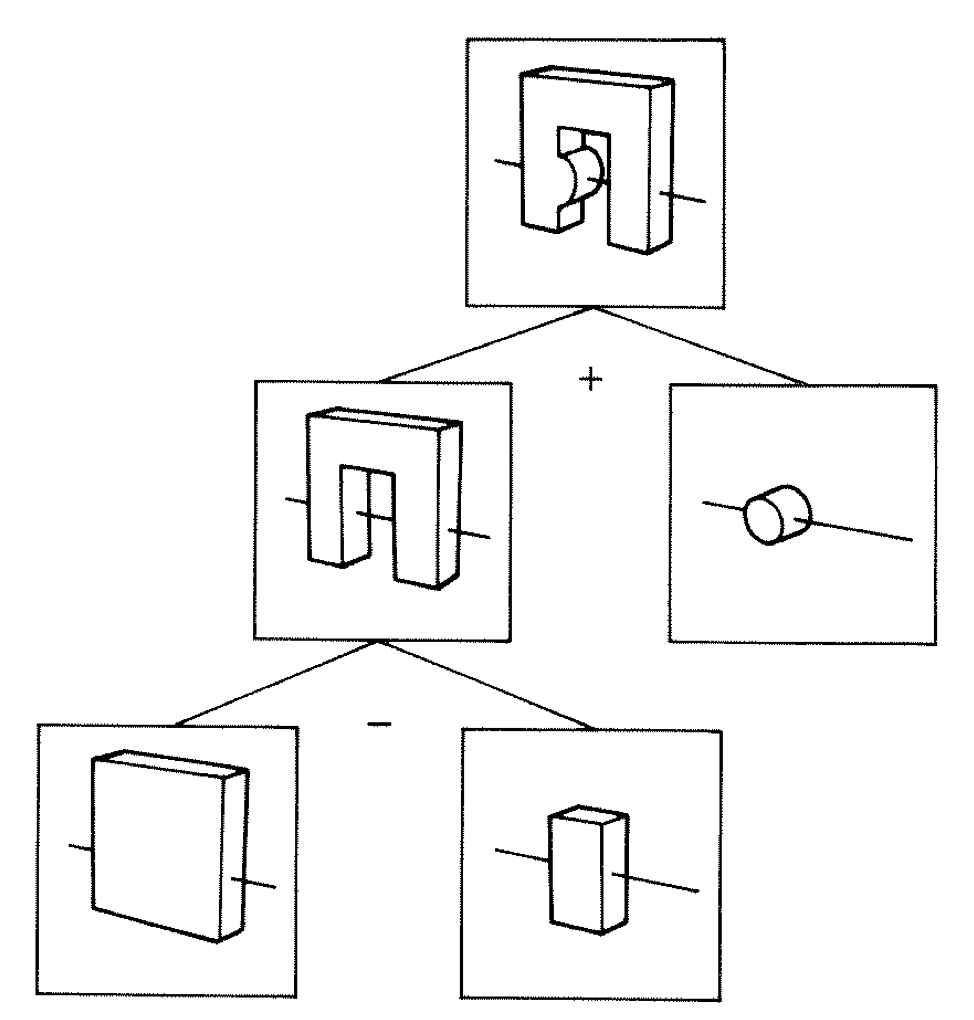
Primitives combined via binary operators
Simple by construction definition, implicit geometry.
- A, B implicit primitive solids
- A + B : union (OR)
- A * B : intersection (AND)
- A - B : difference (AND NOT)
- !B : complement (NOT) (inside <-> outside)
CSG expressions
- non-unique: A - B == A * !B
- represented by binary tree, primitives at leaves
3D Parametric Ray : ray(t) = r0 + t rDir
Ray Geometry Intersection
- primitive : find t roots of implicit eqn
- composite : pick primitive intersect, depending on CSG tree
How to pick exactly ?
CSG : Which primitive intersect to pick ?
In/On/Out transitions
Classical Roth diagram approach
- find all ray/primitive intersects
- recursively combine inside intervals using CSG operator
- works from leaves upwards
Computational requirements:
- find all intersects, store them, order them
- recursive traverse
BUT : High performance on GPU requires:
- massive parallelism -> more the merrier
- low register usage -> keep it simple
- small stack size -> avoid recursion
Classical approach not appropriate on GPU
CSG Complete Binary Tree Serialization -> simplifies GPU side
Bit Twiddling Navigation
- parent(i) = i/2 = i >> 1
- leftchild(i) = 2*i = i << 1
- rightchild(i) = 2*i + 1 = (i << 1) + 1
- leftmost(height) = 1 << height
Geant4 solid -> CSG binary tree (leaf primitives, non-leaf operators, 4x4 transforms on any node)
Serialize to complete binary tree buffer:
- no need to deserialize, no child/parent pointers
- bit twiddling navigation avoids recursion
- simple approach profits from small size of binary trees
- BUT: very inefficient when unbalanced
Height 3 complete binary tree with level order indices:
depth elevation
1 0 3
10 11 1 2
100 101 110 111 2 1
1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111 3 0
postorder_next(i,elevation) = i & 1 ? i >> 1 : (i << elevation) + (1 << elevation) ; // from pattern of bits
Postorder tree traverse visits all nodes, starting from leftmost, such that children are visited prior to their parents.
Evaluative CSG intersection Pseudocode : recursion emulated
fullTree = PACK( 1 << height, 1 >> 1 ) // leftmost, parent_of_root(=0) tranche.push(fullTree, ray.tmin) while (!tranche.empty) // stack of begin/end indices { begin, end, tmin <- tranche.pop ; node <- begin ; while( node != end ) // over tranche of postorder traversal { elevation = height - TREE_DEPTH(node) ; if(is_primitive(node)){ isect <- intersect_primitive(node, tmin) ; csg.push(isect) } else{ i_left, i_right = csg.pop, csg.pop // csg stack of intersect normals, t l_state = CLASSIFY(i_left, ray.direction, tmin) r_state = CLASSIFY(i_right, ray.direction, tmin) action = LUT(operator(node), leftIsCloser)(l_state, r_state) if( action is ReturnLeft/Right) csg.push(i_left or i_right) else if( action is LoopLeft/Right) { left = 2*node ; right = 2*node + 1 ; endTranche = PACK( node, end ); leftTranche = PACK( left << (elevation-1), right << (elevation-1) ) rightTranche = PACK( right << (elevation-1), node ) loopTranche = action ? leftTranche : rightTranche tranche.push(endTranche, tmin) tranche.push(loopTranche, tminAdvanced ) // subtree re-traversal with changed tmin break ; // to next tranche } } node <- postorder_next(node, elevation) // bit twiddling postorder } } isect = csg.pop(); // winning intersect
https://bitbucket.org/simoncblyth/opticks/src/tip/optixrap/cu/csg_intersect_boolean.h
CSG Deep Tree : Positivize tree using De Morgan's laws
Positive form CSG Trees
Apply deMorgan pushing negations down tree
- A - B -> A * !B
- !(A*B) -> !A + !B
- !(A+B) -> !A * !B
- !(A - B) -> !(A*!B) -> !A + B
End with only UNION, INTERSECT operators, and some complemented leaves.
COMMUTATIVE -> easily rearranged
1st step to allow balancing : Positivize : remove CSG difference di operators
... ...
un cy
un cy
un cy
un cy
un cy
di cy
cy cy
... ...
un cy
un cy
un cy
un cy
un cy
in cy
cy !cy